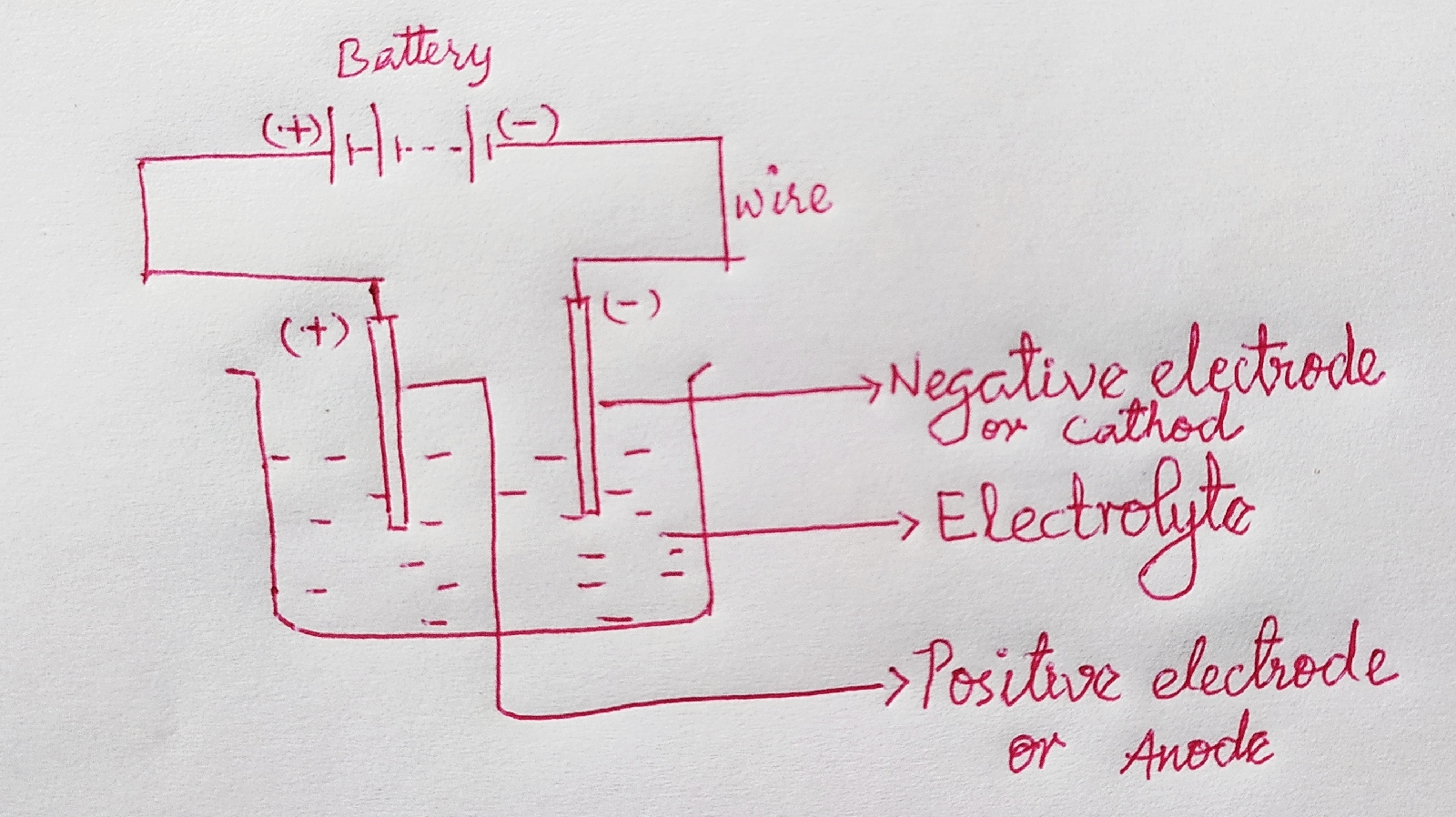
Light NCERT Science Class 8 Summary Note
What Makes Things Visible When light from an object enters our eyes, then we see the object. The light may have been emitted or reflected by the object. Mirror Highly polished surface is called mirror. Reflection Bending back of light ray after falling on a surface, is called reflection. Incident ray The light ray which strikes any surface, is called incident ray. Reflected ray The ray that comes back from the surface after reflection, is called as reflected ray. Normal Line perpendicular to surface at point of incidence of light ray, is called normal. Angle of incidence The angle between normal and incident ray, is called angle of incidence. Angle of reflection The angle between normal and reflected ray, is called angle of reflection. Laws of reflection (i) The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane. (ii) The angle of incidence is always equal to ...