Light NCERT Science Class 8 Summary Note
What Makes Things Visible
When light from an object enters our eyes, then we see the object.
The light may have been emitted or reflected by the object.
Mirror
Highly polished surface is called mirror.
Reflection
Bending back of light ray after falling on a surface, is called reflection.
Incident ray
The light ray which strikes any surface, is called incident ray.
Reflected ray
The ray that comes back from the surface after reflection, is called as reflected ray.
Normal
Line perpendicular to surface at point of incidence of light ray, is called normal.
Angle of incidence
The angle between normal and incident ray, is called angle of incidence.
Angle of reflection
The angle between normal and reflected ray, is called angle of reflection.
Laws of reflection
(i) The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
Nature of Images formed by Plane Mirror
-Plane mirror forms virtual and errect images.
-Size of image = Size of object.
-Object distance = Image distance
-Images show lateral inversion.
Lateral inversion
Inversion of side i.e., left of the object appears on right of image and right of object appears on the left of image.
Types of reflection
(i) Regular reflection
(ii) Irregular or diffused reflection
Regular reflection
-When all parallel rays reflected from a plane surface are parallel, the reflection is known as regular reflection.
OR
When all parallel incident rays form parallel reflected rays, the reflection is known as regular reflection.
-Reflection from smooth surface is regular reflection.
-Images are formed here.
Irregular or diffused reflection
-When all parallel rays reflected from a plane surface are not parallel, the reflection is known as irregular reflection.
OR
When all parallel incident rays do not form parallel reflected rays, the reflection is known as irregular reflection.
-Reflection from rough surface is irregular reflection.
-Images are not formed here.
Periscopes are used in submarines, tanks, bunkers to see things outside.
A plane mirror forms only a single image of an object.
Multiple images are formed when two plane mirrors are used in combination.
White light
Sunlight is referred to as white light.
It consists of seven colours.
Dispersion
Splitting of light into its colours is known as dispersion.
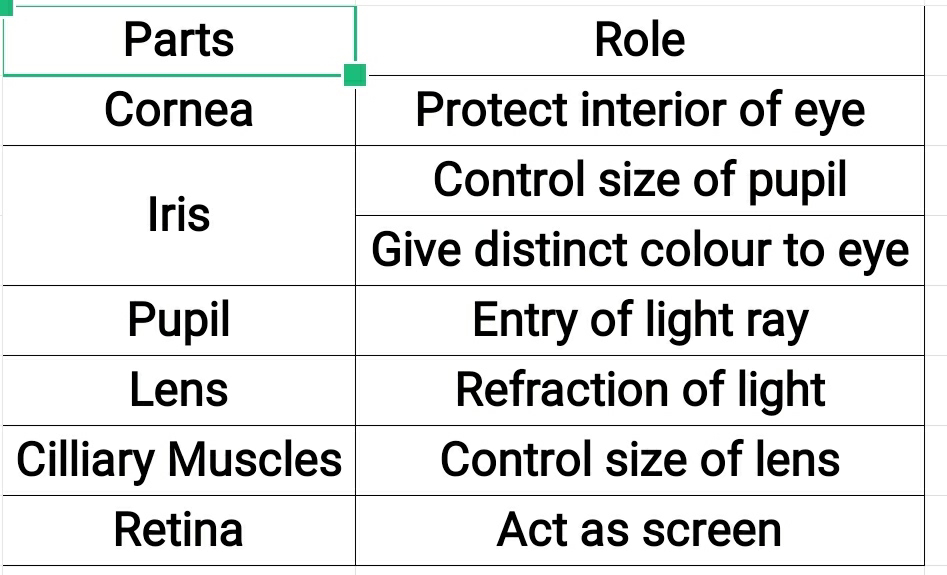
Human eye
Kinds of cells in retina
(i) Cones - These are sensitive to bright light.
- These sense colour.
(ii) Rods- These are sensitive to dim light.
Blind spot
The spot at junction of optic nerve and retina.
There are no sensory cells at the spot.
No vision is possible at the spot.
The impression of an image doesn't vanish immediately from the retina.
It persists there for about 1/16th of a second.
If still images of a moving object are flashed on the eye at a rate faster than 16 per second, then the eye percieves this object as moving.
Eyelids prevent any object or excessive light from entering eye.
Minimum distance of vision - 25cm
Eye defects
Near sightedness
Person can see nearby objects clearly.
Person can't see distant object clearly.
Far sightedness
Person can see distant object clearly.
Person can not see nearby objects clearly.
Cataract
Particularly in old age, eye sight becomes foggy.
Reason- Cloudy lens
Correction of defects
With suitable corrective lenses, these defects can be corrected.
Care of Eyes
-If advised use suitable spectacles.
-Too little or too much light is bad for eyes.
-Do not look at the sun or a powerful light directly.
-Never rub your eyes.
-Wash eyes frequently with clean water.
-Always read at the normal distance for vision.
-Take balanced diet.
Lack of vitamin A in foodstuffs is responsible for many eye troubles.
Few foods rich in vitamin A
Raw carrots, broccoli, green vegetable, cod liver oil etc.
Braille
Popular resource for visually challenged person is Braille.
Comments
Post a Comment