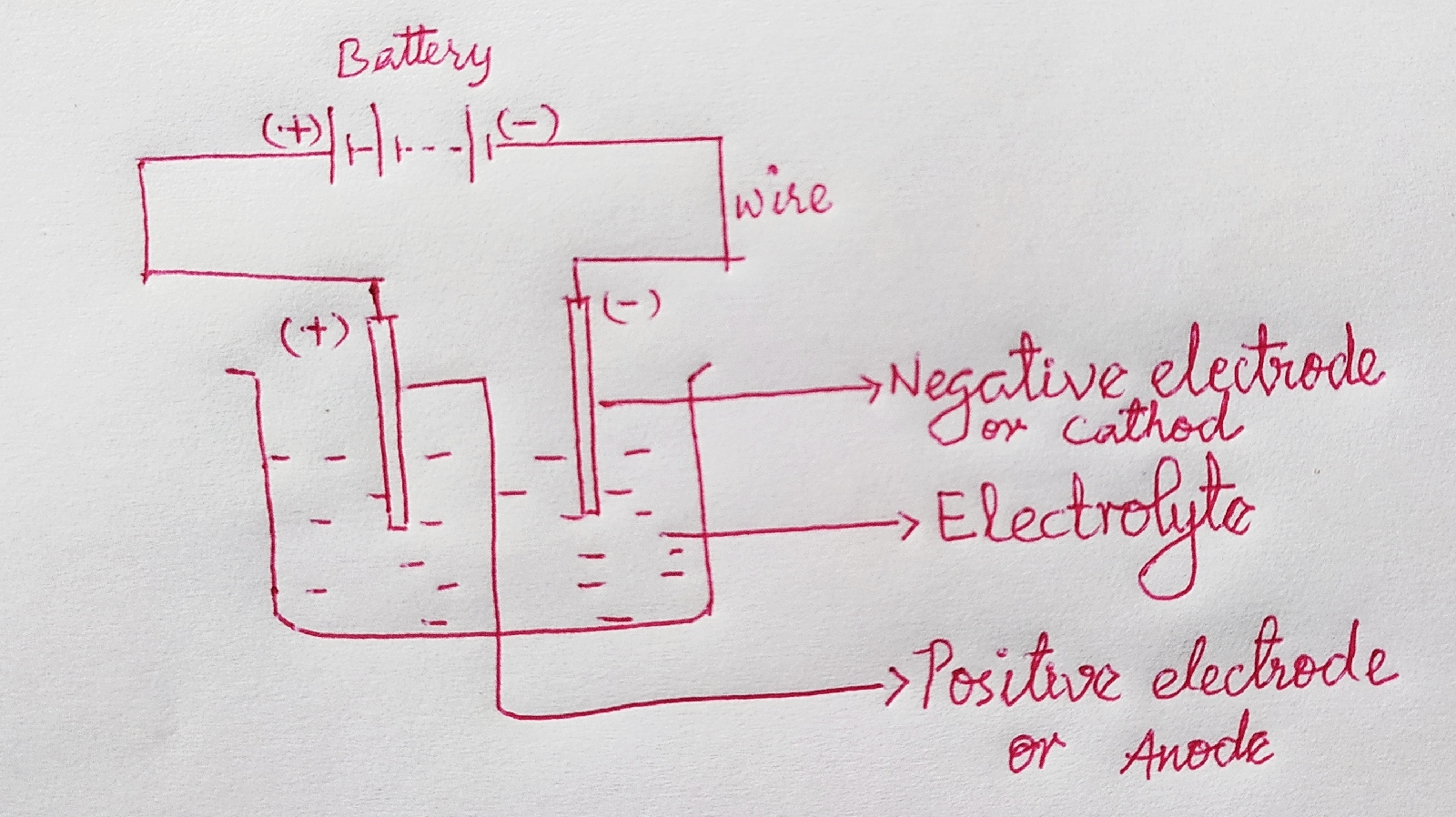
Some Natural Phenomena NCERT Science Class VIII Chapter 15 Summary Note
When we take off clothes in dark, we see a spark and crackling sound. Because - Our body gets rubbed with clothes. - This produces charges. - When charges meet, they cause spark and crackling sound. Charged object Object having electric charge. Example- Rubbed balloon Electric charges are generated by rubbing. Types of charges- (a) Positive charge (b) Negative charge Interaction between charges -Like charges repel each other. -Unlike charges attract each other. It is a convention to call the charge acquired by a glass rod when it is rubbed with silk as positive. The another kind of charge is said to be negative. Static charge Charge that do not move. Electric current Movement of charges , is electric current. Electroscope A device that test whether an object is charged or not, is called electroscope.